Salt Content of Pork Vs Beef

vs

Summary
Turkey meat and pork comprise similar amounts of protein, minerals, and no carbohydrates. Pork contains almost twice as much fats as turkey meat.
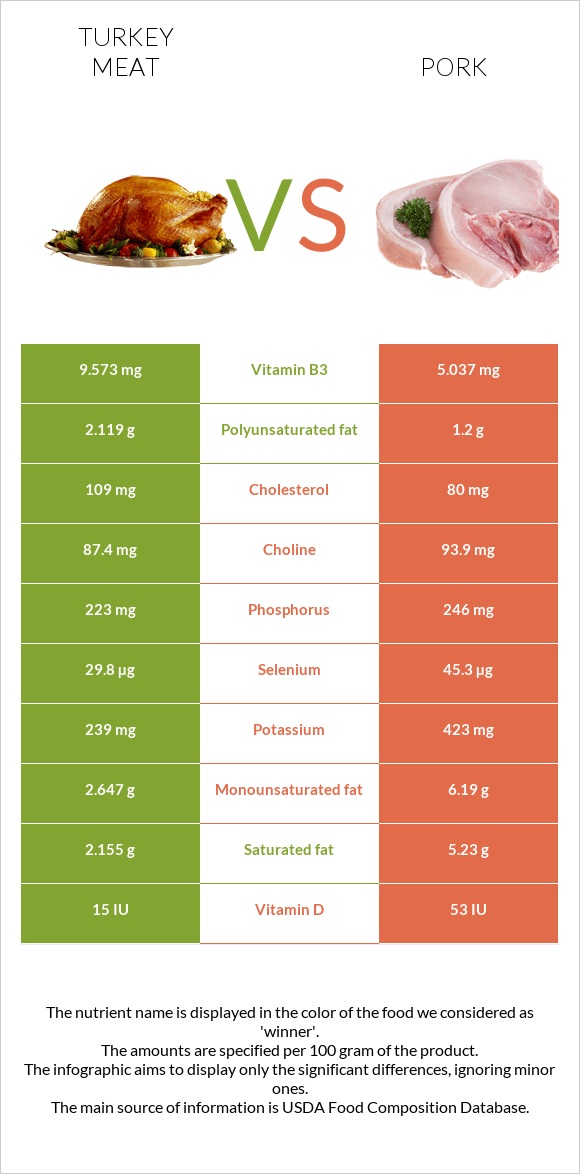
Even though both meats comprise similar amounts of vitamins, turkey meat is 5.6 richer in vitamin A, almost ii times richer in vitamin B3. It is likewise richer in vitamins B5, B6, folate or B9, and B12, atomic number 26, and copper. Pork is 19.5 times richer in vitamin B1, 3.5 times richer in vitamin D and vitamin Due east, also as vitamin B2, calcium, potassium, and phosphorus.
The darker the meat is, the more than saturated fats it contains, leading to mostly agin impacts on health. So, turkey meat has a less negative impact on wellness than pork.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Classification
- Gustation and Use
- Varieties
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients and Calories
- Calories
- Protein and carbohydrates
- Fats and cholesterol
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Glycemic Index
- Acidity
- Weight Loss & Diets
- Wellness Bear upon
- Health Benefits
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Downsides and Risks
- Cardiovascular health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- References
Introduction
The rubber, the value, and, more importantly, the quality of the food makes people hesitate to cull one or another food. Both turkey meat and pork are usually consumed meats. This commodity demonstrates their differences and what they accept in common and discusses their impact on health.
Nomenclature
The main divergence betwixt pork and turkey is based upon their myoglobin content. Every bit pork is high in myoglobin, it is classified as red meat, while turkey as poultry is white meat.
Taste and Utilise
Surprisingly, one study has found that turkey tastes more like pork than chicken. The attributes closely related to each other are its brothy, fatty, salty, sugariness, and umami gustation (1).
The best pork to look for can be described equally greyish pink in color, firm and fine-grained, well-marbled, and covered with an outer layer of house white fatty.
Varieties
Both turkey meat and pork can be produced as candy or fresh meat. Processed meat has a significantly different impact on health when compared to fresh meat.
The dissimilar varieties of turkeys are based on their historic period and are as follows.
- Fryer-Roaster Turkey: a young, immature turkey, usually less than 12 weeks of age.
- Young Turkey: a turkey usually less than half dozen months of historic period.
- Yearling Turkey: a fully matured turkey, usually less than fifteen months of age.
- Mature or Former (Hen or Tom) Turkey: an adult turkey, ordinarily more than 15 months of age (2).
Pork's varieties are based on the cutting. At that place are iv cardinal cuts of pork: the shoulder, the leg or ham, the loin, and the abdomen or the side.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are described for whole, roasted turkey meat and whole, broiled pork loin.
Macronutrients and Calories
Pork is denser in nutrients, containing 58% water than turkey meat which contains 63.five% water.
Both turkey meat and pork take the same average serving size of 85g.
Calories
Both of the meats are high-calorie foods. A hundred grams serving of pork provides 242 calories; meanwhile, turkey meat provides 189 calories.
Protein and carbohydrates
Both of these foods incorporate a very like level of protein. The difference betwixt the amounts of essential amino acids is also minimal. That being said, pork contains slightly more essential amino acids than turkey meat.
Only like other meats, they both contain no carbohydrates.
Fats and cholesterol
Pork contains two times more than fats than turkey meat. Pork is much richer in monounsaturated and saturated fats, while turkey meat contains almost ii times more polyunsaturated fats.
Pork is lower in cholesterol.
Vitamins
Turkey meat is richer in nigh B circuitous vitamins - B3, B5, B6, B9 or folate and B12. Nevertheless, this doesn't utilize to vitamin B2 and especially vitamin B1, which are higher in pork.
Pork is iii times richer in fat-soluble vitamin D and vitamin E merely contains less vitamin A than turkey meat.
Turkey meat is absent in vitamins One thousand, and C. Pork is absent just in vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins past which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below prove how much of the daily needs tin can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
vi
:
v
![]()
Contains more than Vitamin A +457.1%
Contains more than Vitamin B3 +xc.1%
Contains more than Vitamin B5 +35.8%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +32.8%
Contains more Folate +80%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +45.seven%
Contains more Vitamin E +314.3%
Contains more than Vitamin D +225%
Contains more Vitamin C +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +1848.9%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +fourteen.2%
Contains more Vitamin A +457.ane%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +90.one%
Contains more than Vitamin B5 +35.8%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +32.eight%
Contains more Folate +lxxx%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +45.vii%
Contains more Vitamin Eastward +314.3%
Contains more Vitamin D +225%
Contains more Vitamin C +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +1848.nine%
Contains more than Vitamin B2 +fourteen.2%
Minerals
These foods incorporate like amounts of minerals.
Pork is significantly higher in potassium, as well as calcium, and phosphorus compared to turkey meat.
Turkey meat is richer in iron and copper. Turkey also has a high level of sodium.
Both of these meats incorporate almost equal amounts of magnesium and zinc.
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered past 300 grams of the food
![]()
4
:
4
![]()
Contains more Fe +25.iii%
Contains more Copper +27.4%
Contains more Calcium +35.7%
Contains more than Phosphorus +x.3%
Contains more Potassium +77%
Contains less Sodium -39.viii%
Equal in Magnesium - 28
Equal in Zinc - 2.39
Contains more Iron +25.3%
Contains more Copper +27.4%
Contains more Calcium +35.7%
Contains more Phosphorus +10.iii%
Contains more Potassium +77%
Contains less Sodium -39.8%
Equal in Magnesium - 28
Equal in Zinc - 2.39
Glycemic Index
Both turkey meat and pork contain no carbohydrates, so their glycemic index is considered to be 0. To read more well-nigh the glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, you can visit this page.
Acidity
The pH value of a food is a direct function of the free hydrogen ions present in that food. Food acids release hydrogen ions, giving acidic foods their singled-out sour flavor.
Thus, the pH may exist divers as a measure of gratis acerbity. More than precisely, pH is divers as the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration (3).
Pork'south pH range is between 5.3 to 6.9, whereas turkey meat'due south is five.seven - 6.8 (three). According to the numbers, both turkey meat and pork have a slightly acidic or close to neutral pH of 7.
Weight Loss & Diets
Meat is a skillful source of protein, vitamins, and minerals in your diet. However, if you currently eat more than 90g (cooked weight) of red and processed meat a day, the Section of Health advises that you cut it down to 70g (iv).
Turkey meat and pork are high-calorie foods. Pork provides 53 more than calories per every hundred grams serving than turkey meat.
For a low-calorie and low-fat diet, turkey meat is a amend option. Both pork and turkey contain no notable amount of carbohydrates and fit well into a low-carb diet.
A nutrition moderate to depression in ruddy meat, unprocessed and lean, and prepared at moderate temperatures is probably the best pick from the public health point of view (five).
Atkins and keto diets are low-carb diets, and when the body is starved of carbs, the liver produces ketones as an alternating fuel from stored fat; therefore, these meats are great for these diets (six).
These meats are consumed during the Paleo diet as well (vii).
Health Impact
This department will show the benefits and risks of meat consumption on health using scientifically proven or researched information.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Wellness
Eating turkey meat doesn't increase or decrease the risk of heart illness. While in that location's no maximum limit for how much poultry you should eat, it is not directly benign to heart health (8).
Turkey meat is a skillful source of arginine. As with other amino acids, the body uses arginine to make new proteins. Arginine is as well the raw material for making nitric oxide, which relaxes and opens arteries (nine).
Regular inclusion of lean fresh pork in the diet in place of other meats may ameliorate body composition without increasing the gamble of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Body composition can be improved without energy restriction or apparent changes in physical activity levels, total meat, or protein intakes (x).
Diabetes
Higher intakes of poultry were found to predict a reduced risk of type Ii diabetes. The prevention of type 2 diabetes might exist aided past consuming certain foods (for example, green vegetables, fruits and berries, oil and margarine, and poultry) rich in nutrients with hypothesized wellness benefits (11).
The limited evidence suggests a possible negative impact of candy pork on glucose-insulin metabolism and a possible positive impact of pork intake on waist circumference and high-density lipoprotein or "adept" cholesterol. Even so, significant research gaps exist, preventing the drawing of definite conclusions (12).
Cancer
Turkey contains anti-cancer properties. It is a good source of the trace mineral selenium, an essential component required for thyroid hormone metabolism, antioxidant defence force systems, and immune function. Scientific studies take suggested that selenium intake tin bring down cancer incidence. Turkey meat also contains tryptophan, which plays an essential office in strengthening the immune organisation (13).
Downsides and Risks
Cardiovascular health
Unprocessed meat and poultry tin exist included in a eye-salubrious eating blueprint, merely processed meat is not part of a heart-healthy eating pattern; it should exist limited or avoided (14).
Red meat is high in cholesterol and saturated fats and, equally a consequence, increases the gamble for cardiovascular diseases such as heart set on and stroke.
Diabetes
Meats cooked at high temperatures increase the risk of developing type ii diabetes or worsening the disease. A healthier style to melt meats is avoiding loftier-heat or open up flame methods (grilling, barbecuing, broiling, and roasting) or having cursory periods of high heat. Some of the healthy cooking methods are baking, sous-vide, humid, steaming, stewing, and stir-frying.
There was besides an increased risk of weight gain and developing obesity in the frequent users of high-temperature cooking methods (caused by disturbance of fat metabolism), which may contribute to the development of diabetes (15).
Cancer
Eating processed meat increases your risk of bowel, stomach, esophageal, colon cancers. The World Health System has classified candy meats, in this case, pork, every bit a Grouping one carcinogen (known to cause cancer). There is too bear witness of links with pancreatic, prostate, nasopharyngeal, and lung cancers (16,17,eighteen,nineteen).
References
- https://world wide web.researchgate.cyberspace/publication/221837180
- https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/PoultryGradingManual.pdf
- The Importance of Food pH in Commercial Canning Operations
- https://www.nhs.uk/alive-well/eat-well/meat-nutrition/
- https://link.springer.com/commodity/10.1007%2Fs11892-013-0365-0
- https://digitalcommons.andrews.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1848&context=luh-pubs
- https://paleofoundation.com/paleo-nutrition-food-list/
- https://www.heartfoundation.org.au/centre-health-education/protein-and-center-health
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/weblog/turkey-a-healthy-base-of-holiday-meals-201211195550
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3407990/
- https://world wide web.nature.com/articles/1602094
- https://www.turkeyfed.com.au/nigh-turkey/health-benefits/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3792009/
- Meat & Heart Good for you Eating
- How Meat Is Cooked May Affect Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ruby-red meat, processed meat and cancer
- Cancer: Carcinogenicity of the consumption of blood-red meat and processed meat
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23467465/
- https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/meat-fish-and-dairy/
Infographic
Which food is preferable for your nutrition?
![]()
![]()
is improve in case of depression diet
 |  | |
| Low Fats diet | | |
| Low Carbs diet | | |
| Low Calories nutrition | | |
| Low glycemic index nutrition | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamin and Mineral Summary Scores
The summary score is calculated past summing up the daily values contained in 300 grams of the product. Plainly the more than the nutrient fulfills human being daily needs, the more than the summary score is.
Vitamin Summary Score
fifty
![]()
56
![]()
Mineral Summary Score
37
![]()
37
![]()
Macronutrients Comparison
Macronutrient comparison charts compare the amount of protein, total fats, and full carbohydrates in 300 grams of the nutrient. The displayed values show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of nutrient.
Protein
171%
![]()
164%
![]()
Carbohydrates
0%
![]()
0%
![]()
Fats
34%
![]()
64%
![]()
Comparison summary
Which nutrient is lower in Saturated Fat?
![]()
Turkey meat is lower in Saturated Fat (divergence - 3.075g)
Which food contains less Sodium?
![]()
Pork contains less Sodium (difference - 41mg)
Which food is lower in Cholesterol?
![]()
Pork is lower in Cholesterol (difference - 29mg)
Which food is cheaper?
![]()
Pork is cheaper (difference - $1.2)
Which food contains less Sugar?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Sugar (0 g)
Which nutrient is lower in glycemic index?
?
The foods have equal glycemic indexes (0)
Which food is richer in minerals?
?
Information technology cannot be stated which food is richer in vitamins. Encounter the charts below for detailed data. Meet the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information.
Which food is richer in vitamins?
?
It cannot be stated which food is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information.
Source: https://foodstruct.com/compare/turkey-meat-vs-pork

Post a Comment for "Salt Content of Pork Vs Beef"